Dole Food Company v. Patrickson
United States Supreme Court
538 U.S. 468 (2003)
- Written by Megan Petersen, JD
Facts
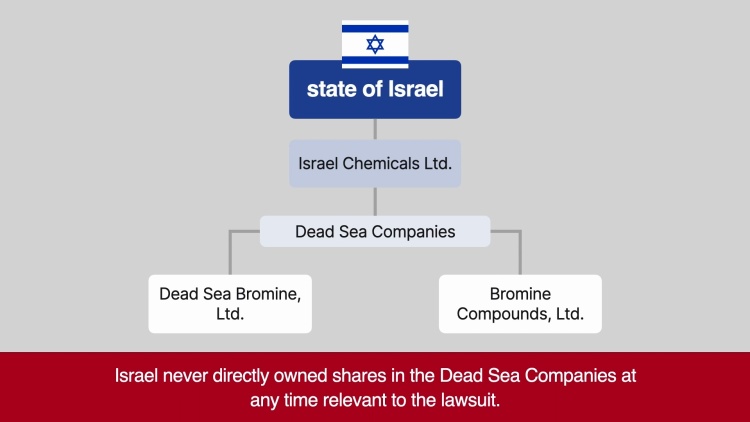
Patrickson (plaintiff) and a group of farm workers from Costa Rica, Ecuador, Guatemala, and Panama, filed suit against Dole Food Company (Dole) (defendant) seeking relief for injuries allegedly caused by pesticides used in their home countries. Dole impleaded two other corporations, Dead Sea Bromine Co., Ltd., and Bromine Compounds, Ltd. (collectively, the Dead Sea Companies) (defendants). The farm workers filed suit in state court in Hawaii. The defendants sought removal of the case to federal court under 28 U.S.C. § 1441(d), which governs removal actions against foreign States and provides that “any civil action brought in a state court against a foreign State as defined [under § 1603(a) of the Foreign State Immunities Act (FSIA)] may be removed by the foreign state to the district court of the United States for the district and division embracing the place where such action is pending.” Section 1603(a) of the FSIA defines “foreign State” to include an “agency or instrumentality of a foreign State.” Additionally, “agency or instrumentality of a foreign State” is defined as an entity which is a separate legal person, corporate or otherwise; and which is an organ of a foreign State or political subdivision thereof, or a majority of whose shares or other ownership interest is owned by a foreign State or political subdivision thereof; and which is neither a citizen of a state of the United States nor created under the laws of any third country. The Dead Sea Companies argued that they were at all times instrumentalities of the State of Israel, and thus were entitled to the same sovereign immunity and removal rights as Israel under the FSIA. The court of appeals held that The Dead Sea Companies were merely a “subsidiary” of an instrumentality (Dole), and were not themselves entitled to instrumentality status. The United States Supreme Court granted certiorari.
Rule of Law
Issue
Holding and Reasoning (Kennedy, J.)
What to do next…
Here's why 907,000 law students have relied on our case briefs:
- Written by law professors and practitioners, not other law students. 47,100 briefs, keyed to 996 casebooks. Top-notch customer support.
- The right amount of information, includes the facts, issues, rule of law, holding and reasoning, and any concurrences and dissents.
- Access in your classes, works on your mobile and tablet. Massive library of related video lessons and high quality multiple-choice questions.
- Easy to use, uniform format for every case brief. Written in plain English, not in legalese. Our briefs summarize and simplify; they don’t just repeat the court’s language.